Reading and writing configuration for Java application using Properties class
- Details
- Written by Nam Ha Minh
- Last Updated on 17 May 2020 | Print Email
This tutorial will help you getting how to use the Properties class for reading and writing configuration for your Java applications. And at the end, we have a sample Swing application that demonstrates reading and writing configuration for database settings.
Table of content:
The java.util.Propertiesclass provides API for reading and writing properties in form of key=value pairs. The properties file can be either in plain text (.properties) format or XML format. For example:
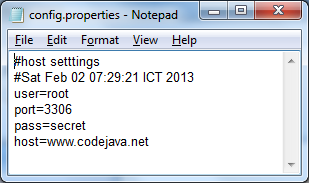
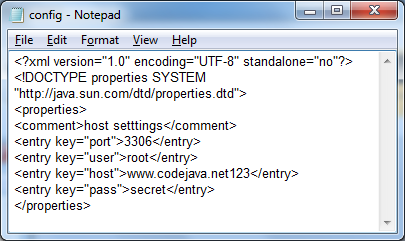
.properties format XML format
First, let’s look at two small examples:
- Loading properties file and reading a property’s value
The following code loads config.properties file and read out a property called “host”:
File configFile = new File("config.properties");
try {
FileReader reader = new FileReader(configFile);
Properties props = new Properties();
props.load(reader);
String host = props.getProperty("host");
System.out.print("Host name is: " + host);
reader.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
// file does not exist
} catch (IOException ex) {
// I/O error
}
- Setting the property’s value and save the properties file
The following code writes value of a property to the config.properties file:
File configFile = new File("config.properties");
try {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("host", "www.codejava.net");
FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(configFile);
props.store(writer, "host settings");
writer.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
// file does not exist
} catch (IOException ex) {
// I/O error
}Now let’s dive into more details for each step: initialize, load, get, set and save.
1. Creating a Properties object
- Create a Propertiesobject by using empty constructor:
Properties props = new Properties();
- Create a Properties object by supplying a default properties list:
Properties defaultProps = new Properties(); // set default properties... // create main Properties object Properties props = new Properties(defaultProps);
The default Properties object would be useful if you want to have a list of default properties which can be used when some properties do not exist in the physical file.
2. Loading properties file
We can load the properties file (.properties or XML) using either subclasses of java.io.Reader class or java.io.InputStream class. Following are some examples:
- Load properties from a .properties file using a FileReader object:
File configFile = new File("config.properties"); FileReader reader = new FileReader(configFile); Properties props = new Properties(); // load the properties file: props.load(reader);The file config.properties must exist in the program’s directory. Of course we can specify absolute path of the configuration file.
- Load properties from a plain text file using an InputStream object:
File configFile = new File("config.properties"); InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(configFile); Properties props = new Properties(); props.load(inputStream);
- If XML is your required format, use the loadFromXML() function:
props.loadFromXML(reader);
Or:props.loadFromXML(inputStream);
- If the properties file is placed in program’s classpath (i.e. in the source package structure or in a jar file), load the input stream as follows:
InputStream inputStream = MyProgram.class.getResourceAsStream("/net/codejava/config/config.properties");
Properties props = new Properties();
props.load(inputStream);NOTE:the methods load()or loadFromXML() do not close the reader nor the input stream, so you should close them afterward:
reader.close();
Or:
inputStream.close();
3. Getting properties values
The Properties class has two methods for retrieving value of a property in the properties file:
- String getProperty(String key): returns value of the property specified by the given key. It returns null if the key not found.
- String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue): like the above method, but this method will return a default value if the key not found.
The following statement gets value of a property whose key is “host”:
String host = props.getProperty("host");And the following statement will return the default value “localhost” if the property not found:
String host = props.getProperty("host", "localhost");NOTE: The method getProperty() searches in the current property list (loaded from the properties) file, then in the default properties list (if specified when constructing the Properties object).
4. Setting properties values
Setting value for a specific property is pretty simple, using this sole method:
Object setProperty(String key, String value)
This method returns previous value of the property specified by the given key.
Example:
props.setProperty("host", "www.codejava.net");NOTE:the method setProperty() does not update the properties file, it just updates the internal properties list.
5. Saving properties file
To save the properties into the file permanently, use the store() method for plain text file and storeToXML() method for XML file. And we have to supply either a java.io.Writer object or an OutputStream object to these methods and also a comment text. Following are some examples:
- Save to plain text file using a Writerobject:
File configFile = new File("config.properties"); FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(configFile); props.store(writer, "host settings"); - Save to XML file using an OutputStream object:
File configFile = new File("config.xml");
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(configFile);
props.storeToXML(outputStream, "host settings");
NOTE:the methods store()or storeToXML() do not close the writer nor the output stream, so you should close them explicitly:
writer.close();
Or:
outputStream.close();
6. Sample Swing application
To demonstrate the usage of Properties class, we create a Swing-based application looks like this:
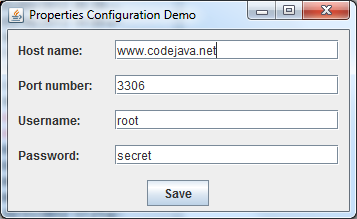
On startup, the program will try to load properties from config.properties file. If the file has not existed before, it will use the default properties. When clicking on the Save button, the properties values will be stored in the config.properties file.
You can download the program’s source code and executable jar file in the attachments section.
Other Java Coding Tutorials:
- 10 Common Mistakes Every Beginner Java Programmer Makes
- 10 Java Core Best Practices Every Java Programmer Should Know
- How to become a good programmer? 13 tasks you should practice now
- How to calculate MD5 and SHA hash values in Java
- How to generate random numbers in Java
- Java File Encryption and Decryption Example
About the Author:
 Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.