JSTL SQL Tag sql:query Example
- Details
- Written by Nam Ha Minh
- Last Updated on 31 August 2019 | Print Email
This post helps you understand how to use the <sql:query> tag in the JSTL SQL tags library with code example.
You know, the <sql:query> tag executes a SQL query and stores the query result in the scoped variable.
JSTL <sql:query> Syntax:
<sql:query
var="<string>"
scope="<string>"
sql="<string>"
dataSource="<string>"
startRow="<string>"
maxRows="<string>"/>
Attributes:
Name | Required | Description |
var | True | Name of the variable to store the query result. This variable is of type javax.servlet.jsp.jstl.sql.Result. |
scope | False | Scope of the var to be placed in. |
sql | False | SQL query to execute. |
dataSource | False | Datasource relative path in the JNDI tree. |
startRow | False | Starting index to show the results. If specified, the results from the index specified here will be displayed. |
maxRows | False | The maximum number of rows to be fetched from the query. |
JSTL <sql:query> Example:
The following JSP code retrieves the records from the citizens table and shows them in tabular form.
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/sql" prefix="sql" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title><sql:query> Demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1><sql:query> Demo</h1>
<sql:setDataSource var="myDS" driver="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"
user="root" password=""/>
<sql:query dataSource="${myDS}" var="citizens">
SELECT * from citizens;
</sql:query>
<table border="1">
<c:forEach var="row" items="${citizens.rows}">
<tr>
<td><c:out value="${row.ssn}"/></td>
<td><c:out value="${row.first_name}"/></td>
<td><c:out value="${row.last_name}"/></td>
<td><c:out value="${row.address}"/></td>
<td><c:out value="${row.telephone}"/></td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
</body>
</html>
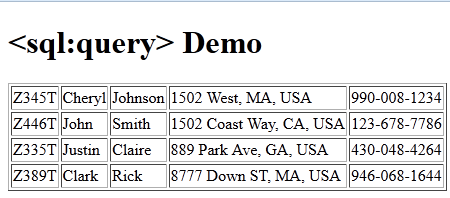
Database (MySQL) Table and Sample Records
The following snippet is the MySQL database sample table and sample data used for the above query.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS citizens (
ssn VARCHAR(10),
first_name VARCHAR(30),
last_name VARCHAR(30),
address VARCHAR(255),
telephone VARCHAR(20)
) engine=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO citizens (ssn, first_name, last_name, address, telephone)
values('Z345T','Cheryl','Johnson','1502 West, MA, USA','990-008-1234');
INSERT INTO citizens (ssn, first_name, last_name, address, telephone)
values('Z446T','John','Smith','1502 Coast Way, CA, USA','123-678-7786');
INSERT INTO citizens (ssn, first_name, last_name, address, telephone)
values('Z335T','Justin','Claire','889 Park Ave, GA, USA','430-048-4264');
INSERT INTO citizens (ssn, first_name, last_name, address, telephone)
values('Z389T','Clark','Rick','8777 Down ST, MA, USA','946-068-1644');
Output:
Recommended Usage of <sql:query> tag:
Having database specific logic in the JSPs (in the presentation layer to be precise) is not a best practice in modern web application development. However, we can take little liberty to do so, provided the application is intended for prototyping or proof of concept (POC).
Other JSTL SQL Tags:
dateParam | param | setDataSource | transaction | update
About the Author:
 Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.