Java exception API hierarchy - Error, Exception and RuntimeException
- Details
- Written by Nam Ha Minh
- Last Updated on 10 February 2025 | Print Email
This article helps you understand about the core classes that make up the Java exception API as well as a list of standard errors and exceptions defined by JDK.
1. Java Exception API Hierarchy
The following diagram describes the class hierarchy of exceptions API in JDK:
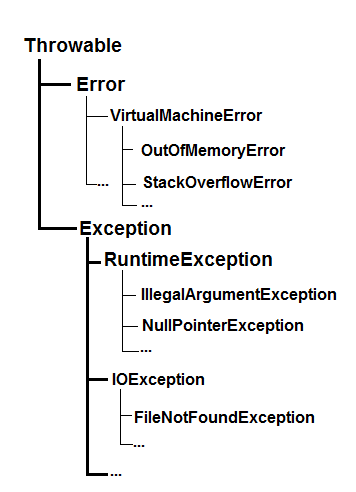
As you can see, Throwable is at the top of the hierarchy. It is the supertype of all exceptions and errors in Java. Below Throwable, there are 3 subtypes:
- Error: represents system errors occurred in abnormal conditions. It is the base class for all errors in Java. Remember that we should not catch errors, because the program cannot be recovered in the events of errors. You may know two well-known errors are StackOverflowError and OutOfMemoryError.
- Exception: is the base class for all exceptions in Java. And most of the time, we throw and catch exceptions which are sub classes of Exception.
- RuntimeException: an exception of this type represents a programming error and typically we should not throw and catch runtime exceptions. NullPointerException is a very well-know runtime exception in Java.
So far we have Error, Exception and RuntimeException represent 3 different kinds of errors and exceptions in JDK. Under them, there are a lot of sub classes and their sub classes. For example, the IOException represents a general I/O error, and its subclass FileNotFoundException is a more specific exception that indicates a file cannot be located on disk. That’s how Java exception API is organized.
2. Common Errors in Java
Here’s a list of common error classes defined by JDK (most of them are under java.lang package):
- AssertionError
- AWTError (java.awt)
- IOError (java.io)
- LinkageError
- ExceptionInInitializerError
- NoClassDefFoundError
- UnsatisfiedLinkError
- VerifyError
- ThreadDeath
- VirtualMachineError
- InternalError
- OutOfMemoryError
- StackOverflowError
- UnknownError
3. Common Exceptions in Java
These exceptions are categorized as checked exceptions and they are grouped by package. The following is a list of common checked exceptions defined in the java.lang package:
- ReflectiveOperationException
- ClassNotFoundException
- InstantiationException
- IllegalAccessException
- InvocationTargetException
- NoSuchFieldException
- NoSuchMethodException
- CloneNotSupportedException
- InterruptedException
4. Common Runtime Exceptions in Java
These exceptions are categorized as unchecked exceptions and they are grouped by package. The following is a list of common unchecked exceptions in the java.lang package:
- ArithmeticException
- IndexOutOfBoundsException
- ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
- StringIndexOutOfBoundsException
- ArrayStoreException
- ClassCastException
- EnumConstantNotPresentException
- IllegalArgumentException
- IllegalThreadStateException
- NumberFormatException
- IllegalMonitorStateException
- IllegalStateException
- NegativeArraySizeException
- NullPointerException
- SecurityException
- TypeNotPresentException
- UnsupportedOperationException
Other Java Exception Handling Tutorials:
- 5 Rules about Catching Exceptions in Java
- Getting Started with Exception Handling in Java
- How to create custom exception in Java
- How to throw exceptions in Java - the differences between throw and throws
- Java Checked and Unchecked Exceptions
- Understanding Exception Stack Trace in Java with Code Examples
- Understanding Java Exception Chaining with Code Examples
- What you may not know about the try-catch-finally construct in Java
About the Author:
 Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Comments