Java Variables Passing Examples - Pass-by-value or Pass-by-reference?
- Details
- Written by Nam Ha Minh
- Last Updated on 21 August 2019 | Print Email
Java always passes variables by value.
Or in other words:Java passes object references to methods by value.
In this article, we will explain why in easy-to-understand fashion with diagrams (we think a picture is worth a thousand words).1. What are Pass-by-value and Pass-by-reference?
First, let’s understand what are pass-by-value and pass-by-reference.Pass-by-value: A copy of the passed-in variable is copied into the argument of the method. Any changes to the argument do not affect the original one.Pass-by-reference: The argument is an alias of the passed-in variable. Any changes to the argument will affect the original one./**
* Impossible Swap function in Java
* @author www.codejava.net
*/
public class Swap {
public static void swap(int x, int y) {
int temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
System.out.println("x(1) = " + x);
System.out.println("y(1) = " + y);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 10;
int y = 20;
swap(x, y);
System.out.println("x(2) = " + x);
System.out.println("y(2) = " + y);
}
}Of course we expect that the swap() method replaces the value of x by y and vice versa. However, unlike other programming languages (C/C++, Pascal, …), the above program prints the following output:x(1) = 20 y(1) = 10 x(2) = 10 y(2) = 20This result proves that the x and y are swapped to each other in the inside the swap() method, however the passed-in variables x and y did not get changed.
2. Understand how reference variables work in Java
To understand why Java passes object references by value, let’s understand how Java manages variables and object references.Each variable is attached to a unique number which represents the physical address of the memory location containing value for that variable. For primitive variable, the memory location stores the actual value of the variable: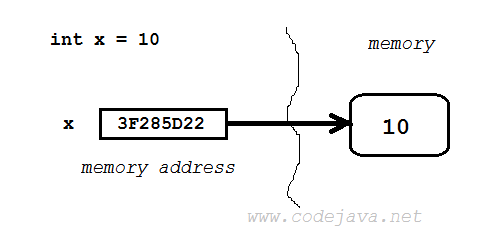 For reference variable, the memory location stores the memory address of the actual object. So reference variable does not store the object itself, it stores only the reference (memory address) to the object. The following diagram illustrates this concept:
For reference variable, the memory location stores the memory address of the actual object. So reference variable does not store the object itself, it stores only the reference (memory address) to the object. The following diagram illustrates this concept: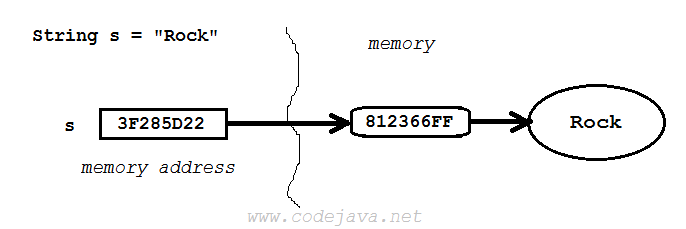
3. Demystifying primitive variables passing in Java
Now let’s come back to the numbers swapping example to understand what happens in the memory.The following picture depicts the memory state before the code in swap() method is executed: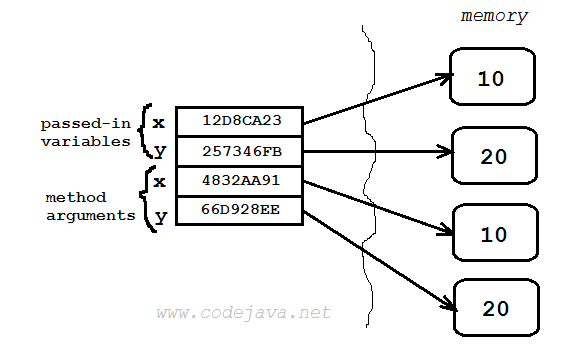 And after the swap() method gets executed:
And after the swap() method gets executed: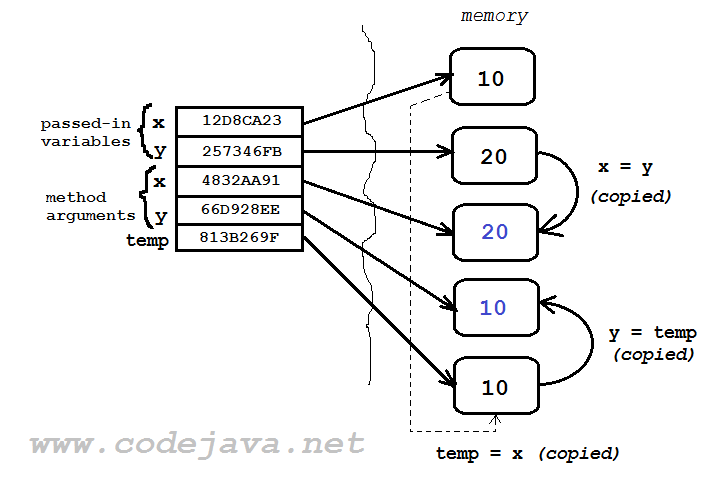 As you can see, only the arguments get changed, and the passed-in variables remain unchanged. It’s because only the values in memory are copied from one location to another, whereas the physical memory address of each variable is fixed.
As you can see, only the arguments get changed, and the passed-in variables remain unchanged. It’s because only the values in memory are copied from one location to another, whereas the physical memory address of each variable is fixed. 4. Demystifying reference variables passing in Java
Next, let’s see how reference variables are passed into a method. Here the version #2 of the swap function:/**
* Impossible Swap function in Java
* @author www.codejava.net
*/
public class SwapObject {
public static void swap(String s1, String s2) {
String temp = s1;
s1 = s2;
s2 = temp;
System.out.println("s1(1) = " + s1);
System.out.println("s2(1) = " + s2);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "You";
String s2 = "Rock";
swap(s1, s2);
System.out.println("s1(2) = " + s1);
System.out.println("s2(2) = " + s2);
}
}The output is similar to the primitive swap function above:s1(1) = Rock s2(1) = You s1(2) = You s2(2) = RockYou see, the s1 and s2 passed-in variables did not get changed after the method execution. Let’s understand what happens in the memory.Here’s the memory state right before the method execution:
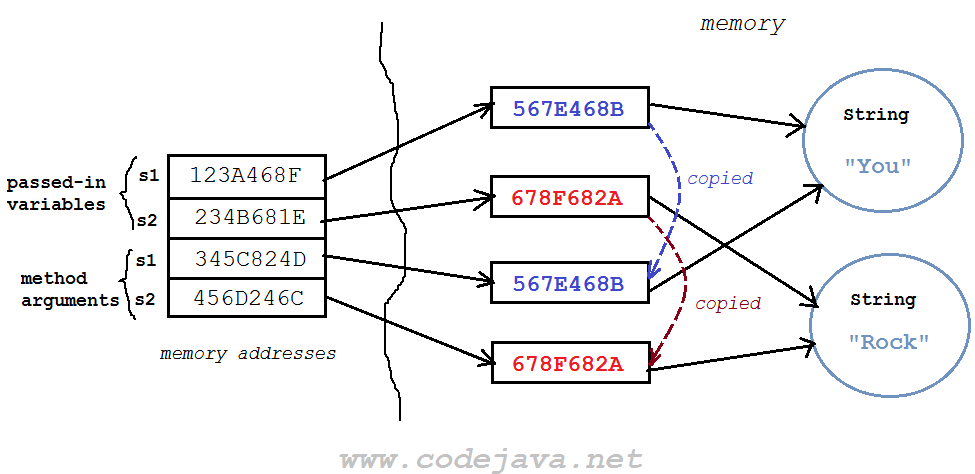 And after the swap() method gets executed:
And after the swap() method gets executed: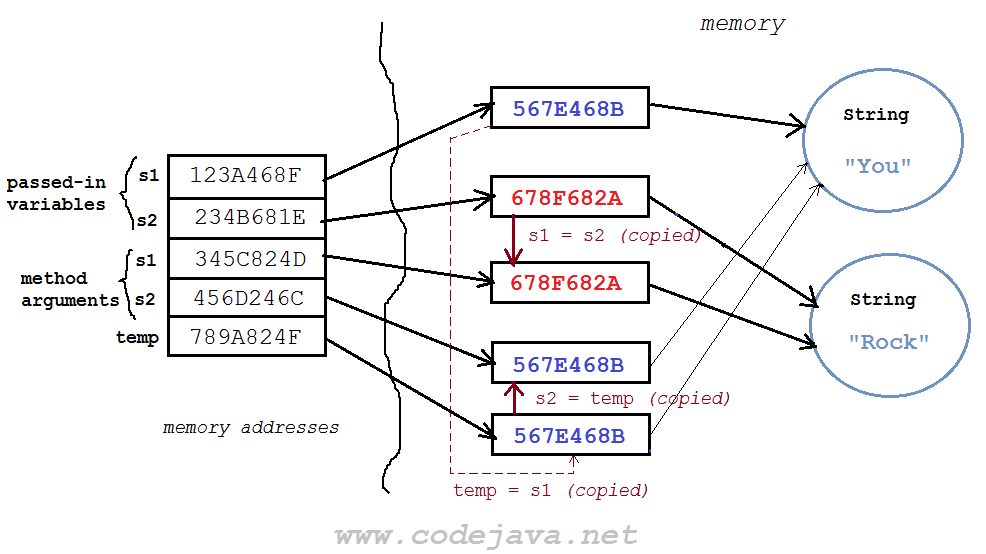 Here, as you can see, the reference variables store values that represent memory addresses of the actual objects they point to. So the method arguments contain the copies of memory addresses of the passed-in variables. That’s why the passed-in variables never get changed in the method. In other words, you cannot change the references that get passed in.From the explanation above, you will be able to understand the tricky code in the next part.
Here, as you can see, the reference variables store values that represent memory addresses of the actual objects they point to. So the method arguments contain the copies of memory addresses of the passed-in variables. That’s why the passed-in variables never get changed in the method. In other words, you cannot change the references that get passed in.From the explanation above, you will be able to understand the tricky code in the next part. 5. Modifying Reference and Changing Reference Examples in Java
Given the Dog class written as below:class Dog {
protected String name;
Dog(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
}Consider the following method that modifies a Dog reference:public void modifyReference(Dog dog) {
dog.setName("Rex");
}and some testing code:Dog dog1 = new Dog("Pun");
System.out.println("Before modify: " + dog1.getName());
modifyReference(dog1);
System.out.println("After modify: " + dog1.getName());The method argument points to the same Dog object as the passed-in reference variable, thus the following output:Before modify: Pun After modify: RexConsider the following method that attempts to change reference of the passed-in parameter:
public void changeReference(Dog dog) {
Dog newDog = new Dog("Poo");
dog = newDog;
}with some testing code:Dog dog2 = new Dog("Meek");
System.out.println("Before change: " + dog2.getName());
tester.changeReference(dog2);
System.out.println("After change: " + dog2.getName());Since it’s impossible to change reference of a passed-in variable within a method, hence the following output:Before change: Meek After change: Meek
6. Conclusion
Java always passes object references to method by value. That means passing the memory address of the object that the variable points to, not passing the variable itself, not the object itself. So we cannot change reference of a passed-in variable in a method. Other Recommended Tutorials:- 9 Rules about Constructors in Java
- 12 Rules and Examples About Inheritance in Java
- 12 Rules of Overriding in Java You Should Know
- 10 Java Core Best Practices Every Java Programmer Should Know
- Understand Interfaces in Java
- Understand abstraction in Java
- Understand encapsulation in Java
- Understand inheritance in Java
- Understand polymorphism in Java
About the Author:
 Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Comments
The "memory", that is the address of the objects get copied, but in reality the Strings, that is the content on the right get copied too.
So there should be 3 Strings "You" and 2 with "Rock".
Am I right?