Java FTP Upload a directory to server
- Details
- Written by Nam Ha Minh
- Last Updated on 19 July 2019 | Print Email
Uploading a single file to a FTP server is not a tricky thing. However, uploading a whole directory is a different story, as it requires some extra work and effort:
- The directory being uploaded may have a quite complex structure, i.e. many directories and files nested together, so we should build an algorithm which is able to iterate over the directory’s content recursively (using recursion algorithm).
- We have to re-create the whole directory structure on the server, then do uploading every single file to its proper location.
In other words, uploading a directory is similar to copy a directory from the local computer to the FTP server, keeping the copied directory’s structure as same as the original one. Here’s the algorithm we’d like to suggest:
- List content of the local directory.
- For each item in the local directory:
- If the item is a file, upload the file to the server.
- If the item is a directory:
- Create the directory on the server.
- Upload this sub directory by repeating the step 1, 2 and 3.
- Return if the directory is empty or if the last item is processed.
To implement the algorithm above, create a utility class looks like this:
public class FTPUtil {
public static void uploadDiretory() throws IOException {
// code to upload a whole directory...
}
public static boolean uploadSingleFile() throws IOException {
// code to upload a single file to the server...
}
}Following is the detailed implementation of the uploadDirectory() method:
/**
* Upload a whole directory (including its nested sub directories and files)
* to a FTP server.
*
* @param ftpClient
* an instance of org.apache.commons.net.ftp.FTPClient class.
* @param remoteDirPath
* Path of the destination directory on the server.
* @param localParentDir
* Path of the local directory being uploaded.
* @param remoteParentDir
* Path of the parent directory of the current directory on the
* server (used by recursive calls).
* @throws IOException
* if any network or IO error occurred.
*/
public static void uploadDirectory(FTPClient ftpClient,
String remoteDirPath, String localParentDir, String remoteParentDir)
throws IOException {
System.out.println("LISTING directory: " + localParentDir);
File localDir = new File(localParentDir);
File[] subFiles = localDir.listFiles();
if (subFiles != null && subFiles.length > 0) {
for (File item : subFiles) {
String remoteFilePath = remoteDirPath + "/" + remoteParentDir
+ "/" + item.getName();
if (remoteParentDir.equals("")) {
remoteFilePath = remoteDirPath + "/" + item.getName();
}
if (item.isFile()) {
// upload the file
String localFilePath = item.getAbsolutePath();
System.out.println("About to upload the file: " + localFilePath);
boolean uploaded = uploadSingleFile(ftpClient,
localFilePath, remoteFilePath);
if (uploaded) {
System.out.println("UPLOADED a file to: "
+ remoteFilePath);
} else {
System.out.println("COULD NOT upload the file: "
+ localFilePath);
}
} else {
// create directory on the server
boolean created = ftpClient.makeDirectory(remoteFilePath);
if (created) {
System.out.println("CREATED the directory: "
+ remoteFilePath);
} else {
System.out.println("COULD NOT create the directory: "
+ remoteFilePath);
}
// upload the sub directory
String parent = remoteParentDir + "/" + item.getName();
if (remoteParentDir.equals("")) {
parent = item.getName();
}
localParentDir = item.getAbsolutePath();
uploadDirectory(ftpClient, remoteDirPath, localParentDir,
parent);
}
}
}
}And here is the detailed implementation of the uploadSingleFile() method:
/**
* Upload a single file to the FTP server.
*
* @param ftpClient
* an instance of org.apache.commons.net.ftp.FTPClient class.
* @param localFilePath
* Path of the file on local computer
* @param remoteFilePath
* Path of the file on remote the server
* @return true if the file was uploaded successfully, false otherwise
* @throws IOException
* if any network or IO error occurred.
*/
public static boolean uploadSingleFile(FTPClient ftpClient,
String localFilePath, String remoteFilePath) throws IOException {
File localFile = new File(localFilePath);
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(localFile);
try {
ftpClient.setFileType(FTP.BINARY_FILE_TYPE);
return ftpClient.storeFile(remoteFilePath, inputStream);
} finally {
inputStream.close();
}
}In order to use the above utility class, we create a test program as follows:
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.commons.net.ftp.FTPClient;
/**
* This test program illustrates how to utilize the FTPUtil class in order
* to upload a whole directory to a FTP server.
* @author www.codejava.net
*
*/
public class FTPUploadDirectoryTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String server = "www.codejava.net";
int port = 21;
String user = "username";
String pass = "password";
FTPClient ftpClient = new FTPClient();
try {
// connect and login to the server
ftpClient.connect(server, port);
ftpClient.login(user, pass);
// use local passive mode to pass firewall
ftpClient.enterLocalPassiveMode();
System.out.println("Connected");
String remoteDirPath = "/Upload";
String localDirPath = "E:/Test/Download/FTP/Test";
FTPUtil.uploadDirectory(ftpClient, remoteDirPath, localDirPath, "");
// log out and disconnect from the server
ftpClient.logout();
ftpClient.disconnect();
System.out.println("Disconnected");
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Supposing you put the Apache Commons Net library jar file into the same directory of the source files, type the following command to compile the utility class and the test program:
javac -cp commons-net-3.6.jar;. FTPUploadDirectoryTest.java
That will also compile the FTPUtil.java file because it is used by the FTPUploadDirectoryTest class.
Type the following command to run the test program:
java -cp commons-net-3.6.jar;. FTPUploadDirectoryTest
If the directory being uploaded E:/Test/Download/FTP/Test has the following structure:
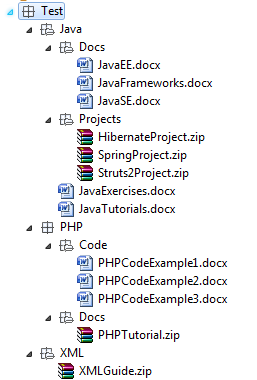
Then the test program will produce the following output:
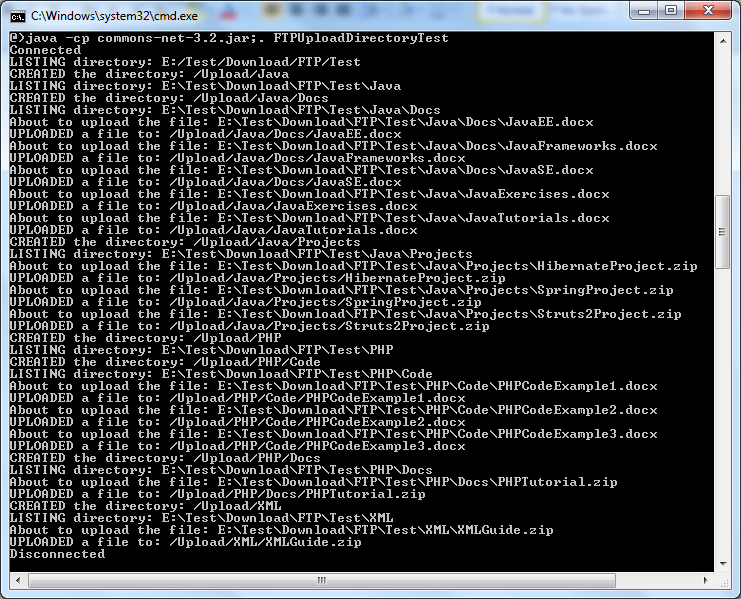
NOTES:
- The solution and code in this article are based on techniques which are described in the following articles:
- You can download the latest distribution of the Apache Commons Net library here.
- If you want to upload only the directory’s structure, see this article: Upload only structure of a directory to FTP server.
Other Java FTP Tutorials:
- Connect and login to a FTP server
- How to remove a non-empty directory on a FTP server
- Java FTP example - Get server's reply messages
- Java FTP example - Change working directory
- Java FTP file download tutorial and example
- Java FTP rename file or directory example
- Java FTP delete file example
About the Author:
 Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.