Java Servlet File Download Example
- Details
- Written by Nam Ha Minh
- Last Updated on 19 May 2020 | Print Email
- Read the file on the server using FileInputStreamclass.
- Determine MIME type of the file by:
- Get the ServletContext via the method getServletContext() method of the servlet.
- Call the method getMimeType(String file) on the ServletContext object to get MIME type of the file.
- Set the following information for the HttpResponseobject:
- Set content type to the MIME type retrieved, by invoking the setContentType(String) method. That tells the browser what kind of the response is.
- Set content length of the response by invoking the setContentLength(int) method.
- Obtains the OutputStream object of the response.
- Read arrays of bytes from the FileInputStream, then write them into the OutputStream. Repeat until no bytes available to read (end of file).
- Close both the FileInputStream and OutputStream.
- The mapping of MIME types is declared by the servlet container. For example, Tomcat declares MIME mapping under section “Default MIME Types Mapping” in this file:
Tomcat install directory\conf\web.xml
- The method getMimeType() returns null if there is no MIME mapping for the specified file. In this case, it is recommended to forcedly set the MIME type to be binary type:
if (mimeType == null) {
mimeType = "application/octet-stream";
} - By default, the browser handles the response based on the content type set in HTTP headers. For example, it will render the image if the response is an image file, or open a PDF reader program if the response is a PDF document, etc. In case we want to force the browser always downloads the file, we can add this header to the response:
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment; filename=\"MyFile.mp4\""); And following is code of the Java servlet called DownloadFileServlet:package net.codejava;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class DownloadFileServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// reads input file from an absolute path
String filePath = "E:/Test/Download/MYPIC.JPG";
File downloadFile = new File(filePath);
FileInputStream inStream = new FileInputStream(downloadFile);
// if you want to use a relative path to context root:
String relativePath = getServletContext().getRealPath("");
System.out.println("relativePath = " + relativePath);
// obtains ServletContext
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
// gets MIME type of the file
String mimeType = context.getMimeType(filePath);
if (mimeType == null) {
// set to binary type if MIME mapping not found
mimeType = "application/octet-stream";
}
System.out.println("MIME type: " + mimeType);
// modifies response
response.setContentType(mimeType);
response.setContentLength((int) downloadFile.length());
// forces download
String headerKey = "Content-Disposition";
String headerValue = String.format("attachment; filename=\"%s\"", downloadFile.getName());
response.setHeader(headerKey, headerValue);
// obtains response's output stream
OutputStream outStream = response.getOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[4096];
int bytesRead = -1;
while ((bytesRead = inStream.read(buffer)) != -1) {
outStream.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
inStream.close();
outStream.close();
}
}Configure URL mapping for this servlet in the web deployment descriptor file web.xml as follows:<servlet> <description>This servlet sends file to client</description> <display-name>DownloadFileServlet</display-name> <servlet-name>DownloadFileServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>net.codejava.DownloadFileServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>DownloadFileServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/DownloadFileServlet</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>Or use the @WebServlet annotation in Servlet 3.0:
@WebServlet("/DownloadFileServlet")
public class DownloadFileServlet extends HttpServlet {
// code of the servlet...
} We can invoke the servlet in the following form of URL:http://localhost:8080/MyWebApp/DownloadFileServlet
The browser should ask the user to download the file as shown in the following screenshot: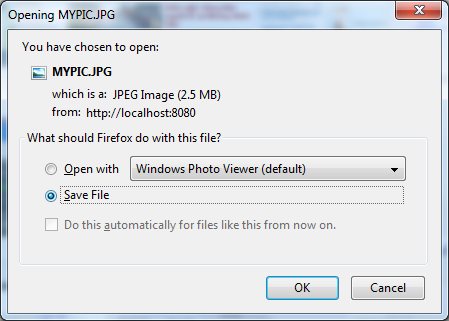
Related Java File Dowload Tutorials:
- Java Servlet File Download from Database Example
- Use HttpURLConnection to download file from an HTTP URL
- Java FTP file download tutorial and example
- Swing application to download files from HTTP server with progress bar
- Swing application to download files from FTP server with progress bar
- Spring MVC sample application for downloading files
- Sample Struts application for downloading files
Other Java Servlet Tutorials:
- Java Servlet Quick Start for beginners (XML)
- Java Servlet for beginners (annotations)
- Handling HTML form data with Java Servlet
- How to use Cookies in Java web application
- How to use Session in Java web application
- How to Handle Error in Web.xml for Java web applications
About the Author:
 Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Comments
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
sdf.setLenient(true);
binder.registerCustomEditor(Date.class, new CustomDateEditor(sdf, true));}
OutputStream out = response.getOutputStream();
JasperExportManager.exportReportToPdfStream(jasperPrint,out);}
JasperReport jasperReport = JasperCompileManager.compileReport(inputStream);
Map params = new HashMap();
String reziser="";
reziser=predstave.get(0).getReziser().getIme()+" "+predstave.get(0).getReziser().getPrezime();
if(predstave!=null && predstave.size()>0)
params.put("reziser", reziser);
public void generisiIzvestaj(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
List predstave = (List)request.getSession().getAttribute("predstave");
response.setContentType("text/html");
JRBeanCollectionDataSource dataSource = new JRBeanCollectionDataSource(predstave);
params.put...
JasperPrint jasperPrint = JasperFillManager.fillReport(jasperReport, params, dataSource);
inputStream.close();
OutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
JasperExportManager.exportReportToPdfStream(jasperPrint, outputStream);
}