How to code and deploy Java XML Web Services (JAX-WS) on Tomcat
- Details
- Written by Nam Ha Minh
- Last Updated on 21 December 2019 | Print Email
In this tutorial, you will learn how to code a Java web application that hosts Java XML web services (JAX-WS) running on Apache Tomcat server. This tutorial focuses on project configuration that enables clients to access web services deployed on Tomcat. So for the details of creating Java XML/SOAP web services, please refer to this tutorial.
1. Add JAX-WS Runtime Dependency
First, add the following dependency to the project’s pom.xml file if Maven is used:
<dependency> <groupId>com.sun.xml.ws</groupId> <artifactId>jaxws-rt</artifactId> <version>2.3.2</version> </dependency>
This will download the JAR files required to compile and run Java XML web services in servlet environment.
2. Create a simple XML/SOAP Web Service
Let’s create a simple Java XML web service class as below:
package net.codejava;
import javax.jws.WebMethod;
import javax.jws.WebService;
import javax.jws.soap.SOAPBinding;
import javax.jws.soap.SOAPBinding.Style;
@WebService
@SOAPBinding(style = Style.RPC)
public class Hello {
@WebMethod
public String bonjour(String name) {
return String.format("Bonjour %s", name);
}
}As you can see, this web service class implements a webservice method that returns a French greeting message followed by a name supplied by the client.
3. Configure Web Services Endpoints
To allow the web services to be discoverable by clients, we need to declare endpoints in JAX-WS descriptor file. Create the sun-jaxws.xml file under WEB-INF directory with the following code:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<endpoints xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/jax-ws/ri/runtime" version="2.0">
<endpoint
name="HelloWebService"
implementation="net.codejava.Hello"
url-pattern="/ws/hello"/>
</endpoints>Here, you declare an <endpoint> element for each web service class. The implementation attribute is for the fully-qualified class name of the web service class, and the url-pattern attribute specifies a URL relative to the web application’s context path. So in this configuration, the web service can be accessed via this URL: http://hostname/appname/ws/hello.
In case you need to declare multiple endpoints, for example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<endpoints xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/jax-ws/ri/runtime" version="2.0">
<endpoint
name="HelloWebService"
implementation="net.codejava.Hello"
url-pattern="/ws/hello"/>
<endpoint
name="ProductWebService"
implementation="net.codejava.Product"
url-pattern="/ws/product"/>
</endpoints>
4. Configure JAX-WS Listener and Servlet
Finally, add the following XML code into the web deployment descriptor file (web.xml):
<listener> <listener-class> com.sun.xml.ws.transport.http.servlet.WSServletContextListener </listener-class> </listener> <servlet> <servlet-name>JAXWSServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class> com.sun.xml.ws.transport.http.servlet.WSServlet </servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>JAXWSServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/ws/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
This configuration enables JAX-WS runtime to handles requests from the clients that invoke the web service endpoints. Note that that URL pattern of JAXWSServlet should be configured in a way that does not conflict with URL patterns other servlets.
5. Code a Web Services Client Test Program
Now, you can start Tomcat server. Open a browser and access the URL http://localhost:8080/SoapTest/ws/hello, you will see the following page appears:
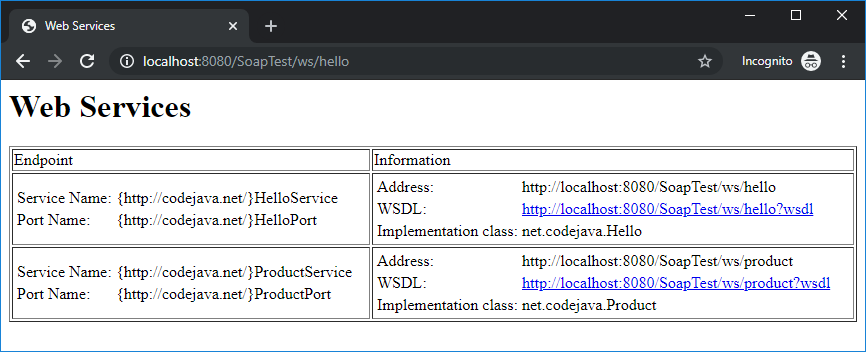
This means the Java web services were deployed successfully on Tomcat and ready to accept client’s requests. And let’s code a Java client program (create a different project) to call the web services.
Open a Command prompt or Terminal window, and type the following command to generate code for the webservice client program:
wsimport -keep -p net.codejava.test http://localhost:8080/SoapTest/ws/hello?wsdl
The wsimport tool is provided in the JDK’s bin directory. Copy the generated Java source files Hello.java and HelloService.java into the new project, and code the client program as follows:
package net.codejava.test;
public class HelloTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloService service = new HelloService();
Hello hello = service.getHelloPort();
String response = hello.bonjour("Chef");
System.out.println(response);
}
}Note that you also need to use the JAX-WS runtime dependency for the client project (if JDK version > 9). Run this client program and you should see the following output:
Bonjour Chef
Congratulations! You have successfully coded and deployed Java XML web services on Apache Tomcat server. For reference, you can download the sample project in the Attachments section below.
You may like to follow the video below:
Other Java Web Services Tutorial:
- Java RESTful Web Services Tutorial for Beginner with Jersey and Tomcat
- Java CRUD RESTful Web Services Examples with Jersey and Tomcat
- Java Client Server Web Services (JAX-WS) Tutorial
- Java Web Services Tutorial using Apache Axis2, Ant and Tomcat
- Monitoring SOAP Messages using TCP/IP Monitor in Eclipse
- Using MTOM to optimize binary data transfer with JAX-WS web services
- Java Web Services Binary Data Transfer Example (base64 encoding)
About the Author:
 Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Comments