JTextField basic tutorial and examples
- Details
- Written by Nam Ha Minh
- Last Updated on 06 July 2019 | Print Email
1. Creating a JTextField object
When creating a text field component, it’s common to specify some initial text and/or a number of columns from which the field’s width is calculated.- Create a text field with some initial text:
JTextField textField = new JTextField("This is a text");
Image:
- Create a text field with a specified number of columns:
JTextField textField = new JTextField(20);
Image:
- Create a text field with both initial text and number of columns:
JTextField textField = new JTextField("This is a text", 20);
Image:
- Create a default and empty text field then set the text and the number of columns later:
JTextField textField = new JTextField();
textField.setText("This is a text");
textField.setColumns(20); NOTE:- If the initial text is not specified, its default value is null (the text field is empty).
- If the number of columns is not specified, its default value is 0 (then the text field’s width is calculated based on the initial text).
2. Adding the text field to a container
- A JTextField can be added to any container like JFrame, JPanel, JDialog or JApplet:
frame.add(textField); dialog.add(textField); panel.add(textField); applet.getContentPane().add(textField);
- Add a JTextField to the container with a specific layout manager:
frame.add(textField, BorderLayout.CENTER); panel.add(textField, gridbagConstraints);
3. Getting or setting content of the text field
- Getting all content:
String content = textField.getText();
- Getting a portion of the content:
int offset = 5; int length = 10; try { content = textField.getText(offset, length); } catch (BadLocationException ex) { // invalid offset/length }That will return 10 characters from position 5th in the text. - Setting content:
textField.setText("another text"); 4. Setting tooltip text for JTextField
Set tooltip for the text field as follows:textField.setToolTipText("Please enter some text here"); Image: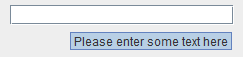 We can also set HTML for the tooltip text:
We can also set HTML for the tooltip text:textField.setToolTipText("<html><b><font color=red>"
+ "Please enter some text here" + "</font></b></html>"); Image: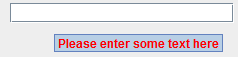
5. Setting input focus for JTextField
Normally, the text field gets focused when the user is clicking on it or pressing the TAB key. To set input focus programmatically, use the following code:
- Setting input focus initially just after the container (such as a JFrame) is displayed:
frame.setVisible(true); textField.requestFocusInWindow();
- Setting input focus at any time: It’s recommend to request the focus inside a SwingUtilities.invokeLater() call:
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
textField.requestFocusInWindow();
}
});6. Adding event listeners for JTextField
- We can capture the event in which the user hits Enter key while typing in the text field. For example:
textField.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { System.out.println("The entered text is: " + textField.getText()); } }); - Capture key events which happen while the user is typing into the text field:
textField.addKeyListener(new KeyListener() {
@Override
public void keyTyped(KeyEvent event) {
System.out.println("key typed");
}
@Override
public void keyReleased(KeyEvent event) {
System.out.println("key released");
}
@Override
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent event) {
System.out.println("key pressed");
}
});
The order of key events is key pressed, key typed and key released. We can use this technique to validate field’s content on-the-fly. In the following example, we check the field’s content whenever the user is typing. If the content is empty, disable the action button; otherwise enable the button:
textField.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter() {
public void keyReleased(KeyEvent event) {
String content = textField.getText();
if (!content.equals("")) {
button.setEnabled(true);
} else {
button.setEnabled(false);
}
}
});
NOTE: In this case, we use the KeyAdapterclass which implements the KeyListener interface, so we have to override only the method we want.7. Working with text selection in JTextField
We can programmatically select the text field’s content.
- Select all text:
textField.selectAll();
Image:
- Select only a portion of text:
textField.setSelectionStart(8); textField.setSelectionEnd(12);
Image:
- Set color for the selection and the selected text:
textField.setSelectionColor(Color.YELLOW); textField.setSelectedTextColor(Color.RED);
Image:
- Set position of the caret and its color:
textField.setCaretColor(Color.RED); textField.setCaretPosition(10);
Image:
8. Customizing JTextField’s appearance
- Disable editing the field’s content:
textField.setEditable(false);
Image:
- Set horizontal alignment of text:
textField.setHorizontalAlignment(JTextField.CENTER);
Image:
Valid values for the method setHorizontalAlignment() are:JTextField.LEFT JTextField.CENTER JTextField.RIGHT JTextField.LEADING JTextField.TRAILING
- Set font style, background color and foreground color:
textField.setFont(new java.awt.Font("Arial", Font.ITALIC | Font.BOLD, 12));
textField.setForeground(Color.BLUE);
textField.setBackground(Color.YELLOW);Image:
9. JTextField demo program
For your reference and testing purpose, we created a simple demo program looks like this:
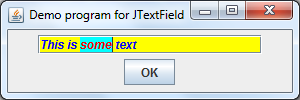
When you are typing something in the text field and hit Enter, the following message dialog appears:
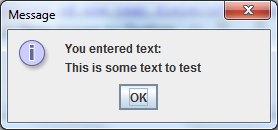
If the field is empty, the OK button is disabled:
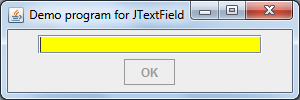
And when clicking the button:
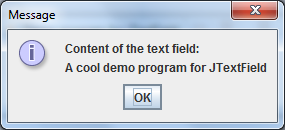
You can download, run and view source code of this program in the attachment section.
Other Java Swing Tutorials:
- Java Swing Hello World Tutorial for Beginners Using Text Editor
- JFrame basic tutorial and examples
- JPanel basic tutorial and examples
- JButton basic tutorial and examples
- JComboBox basic tutorial and examples
- JCheckBox basic tutorial and examples
- JList basic tutorial and examples
- JTree basic tutorial and examples
About the Author:
 Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Comments
Check this article: codejava.net/.../...