Hibernate Many-to-Many XML Mapping Example
- Details
- Written by Nam Ha Minh
- Last Updated on 16 July 2019 | Print Email
This Hibernate tutorial is going to teach you how to model a bidirectional many-to-many association using XML schema. The following entity relationship diagram illustrates a typical many-to-many association:
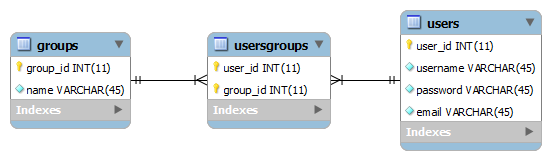
A many-to-many association
We are going to develop a sample Hibernate application that manages the above association in which a user may belong to many groups, and a group may contain many users. The UsersGroups is the join table between the groups and users tables.
The following pieces of software/library are used in this tutorial:
Table of content:
1. Creating Database and Tables
We will create a MySQL database called usersdb and three tables: users, groups and UsersGroups (join table). If you are using MySQL Workbench program, executing the following script in its SQL Editor:
create database usersdb; use usersdb; CREATE TABLE `users` ( `user_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `username` varchar(45) NOT NULL, `password` varchar(45) NOT NULL, `email` varchar(45) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`user_id`) ); CREATE TABLE `groups` ( `group_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(45) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`group_id`) ); CREATE TABLE `UsersGroups` ( `user_id` int(11) NOT NULL, `group_id` int(11) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`user_id`,`group_id`), KEY `fk_user` (`user_id`), KEY `fk_group` (`group_id`), CONSTRAINT `fk_user` FOREIGN KEY (`user_id`) REFERENCES `users` (`user_id`), CONSTRAINT `fk_group` FOREIGN KEY (`group_id`) REFERENCES `groups` (`group_id`) );
Or type the following command in case you are using MySQL Command Line Client program:
source Path\To\The\Script\File\MySQLscript.sql
In which the MySQLscript.sql file can be created from the above script or picked up from the attached project. The newly created database would have the following structure:
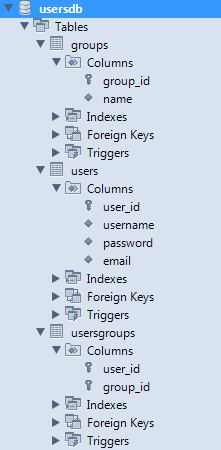
2. Setting up an Eclipse project
In Eclipse IDE, create a standard Java project named HibernateMany2ManyXMLExample with the following structure:
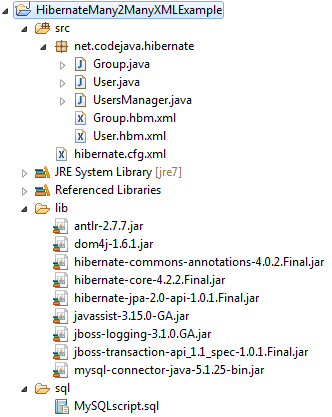
As we can see, the project contains the following files:
- Model classes: Group.java and User.java
- Hibernate XML mapping files: Group.hbm.xmland User.hbm.xml
- Hibernate XML configuration file: hibernate.cfg.xml
- Test program: UsersManager.java
- Hibernate required JAR libraries and MySQL Connector Java driver:
- hibernate-core-4.2.2.Final.jar
- hibernate-commons-annotations-4.0.2.Final.jar
- mysql-connector-java-5.1.25-bin.jar
- jboss-transaction-api_1.1_spec-1.0.1.Final.jar
- hibernate-jpa-2.0-api-1.0.1.Final.jar
- jboss-logging-3.1.0.GA.jar
- antlr-2.7.7.jar
- dom4j-1.6.1.jar
- javassist-3.15.0-GA.jar
- MySQL script file: MySQLscript.sql
The Hibernate and MySQL Connector/J jar files can be found from their distribution archives.
3. Coding Hibernate Model Classes
Create two JavaBean-style model classes corresponding to the groups and users tables as follows:
File net\codejava\hibernate\Group.java:
package net.codejava.hibernate;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Group {
private long id;
private String name;
private Set<User> users = new HashSet<User>();
public Group(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void addUser(User user) {
this.users.add(user);
}
// setters and getters
}
File net\codejava\hibernate\User.java:
package net.codejava.hibernate;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class User {
private long id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String email;
private Set<Group> groups = new HashSet<Group>();
public User(String username, String password, String email) {
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.email = email;
}
public void addGroup(Group group) {
this.groups.add(group);
}
// setters and getters
}NOTES: For a bidirectional many-to-many association, we should specify a collection of another side from each side (using java.util.Set implementation in this tutorial). For example:
- A Group has a set of Users.
- A User has a set of Groups.
And note that the methods addUser(User) and addGroup(Group) were added to make adding items to the collection easily.
4. Writing Hibernate Mapping Files
To map the above model classes with the database tables, create two Hibernate mapping files Group.hbm.xml and User.hbm.xml as follows:
File net\codejava\hibernate\Group.hbm.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping package="net.codejava.hibernate">
<class name="Group" table="GROUPS">
<id name="id" column="GROUP_ID">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="name" column="NAME" />
<set name="users" table="UsersGroups" cascade="save-update">
<key column="GROUP_ID"/>
<many-to-many column="USER_ID" class="User" />
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
File net\codejava\hibernate\User.hbm.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping package="net.codejava.hibernate">
<class name="User" table="USERS">
<id name="id" column="USER_ID">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="username" column="USERNAME" />
<property name="password" column="PASSWORD" />
<property name="email" column="EMAIL" />
<set name="groups" table="UsersGroups" inverse="true">
<key column="USER_ID"/>
<many-to-many column="GROUP_ID" class="Group" />
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
NOTES:
- We have to specify name of the join table (UsersGroups) in the <set> element.
- The attribute inverse=”true” can be placed on either side to specify which is owner of the relationship. In the mapping above, the relationship owner is the Group (because inverse=”true” is set on the User side).
- The attribute cascade=”save-update” on the Group side tells Hibernate to update the children (users) when the parent (group) is saved or updated.
- We don’t have to create model class/mapping file for the join table.
5. Writing Hibernate Configuration File
We need to tell Hibernate which database type and mapping files needs to be used, so create the Hibernate configuration file (hibernate.cfg.xml) with the following content:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- Database connection settings -->
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/usersdb</property>
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.password">secret</property>
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<mapping resource="net/codejava/hibernate/User.hbm.xml"/>
<mapping resource="net/codejava/hibernate/Group.hbm.xml"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>NOTES: Change the username and password according to your MySQL account.
6. Coding a Test Program
Following is a test program that persists the following entities and relationship:
- Administrator Group > User 1
- Administrator Group > User 2
- Guest Group > User 1
Here is the source code:
package net.codejava.hibernate;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistryBuilder;
/**
* A program that demonstrates using Hibernate framework to manage
* a bidirectional many-to-many association in relational database.
* @author www.codejava.net
*
*/
public class UsersManager {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// loads configuration and mappings
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
ServiceRegistryBuilder registry = new ServiceRegistryBuilder();
registry.applySettings(configuration.getProperties());
ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry = registry.buildServiceRegistry();
// builds a session factory from the service registry
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration
.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
// obtains the session
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction();
Group groupAdmin = new Group("Administrator Group");
Group groupGuest = new Group("Guest Group");
User user1 = new User("Tom", "tomcat", "tom@codejava.net");
User user2 = new User("Mary", "mary", "mary@codejava.net");
groupAdmin.addUser(user1);
groupAdmin.addUser(user2);
groupGuest.addUser(user1);
user1.addGroup(groupAdmin);
user2.addGroup(groupAdmin);
user1.addGroup(groupGuest);
session.save(groupAdmin);
session.save(groupGuest);
session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close();
}
}
Output of the program:
Hibernate: insert into GROUPS (NAME) values (?)
Hibernate: insert into USERS (USERNAME, PASSWORD, EMAIL) values (?, ?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into USERS (USERNAME, PASSWORD, EMAIL) values (?, ?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into GROUPS (NAME) values (?)
Hibernate: insert into UsersGroups (GROUP_ID, USER_ID) values (?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into UsersGroups (GROUP_ID, USER_ID) values (?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into UsersGroups (GROUP_ID, USER_ID) values (?, ?)
Result in the groups table:
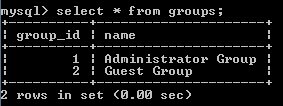
Result in the users table:
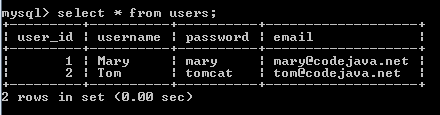
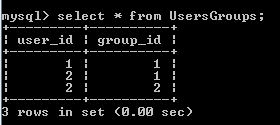
Result in the UsersGroups table:
Related Hibernate Many-to-Many Tutorials:
- Hibernate Many-to-Many Association Annotations Example
- Hibernate Many-to-Many Association with Extra Columns in Join Table Example
Other Hibernate Tutorials:
- Java Hibernate JPA Annotations Tutorial for Beginners
- Hibernate One-to-One Association on Primary Key Annotations Example
- Hibernate One-to-Many Association Annotations Example
- Hibernate Enum Type Mapping Example
- Hibernate Binary Data and BLOB Mapping Example
- Hibernate Query Language (HQL) Example
- Java Hibernate Reverse Engineering Tutorial with Eclipse and MySQL
- Hibernate Basics - 3 ways to delete an entity from the datastore
About the Author:
 Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Comments
But then all data in this table will be the same.
how can I resolve following use case ? what if I want to have data on the connector table 'usergroups' which are related to the user object ?