Hibernate One-to-One With Primary Key XML Mapping Example
- Details
- Written by Nam Ha Minh
- Last Updated on 12 December 2023 | Print Email
This Hibernate tutorial is going to provide an example application that manages a bidirectional one-to-one association on a primary key which is described by the following entity relationship diagram:
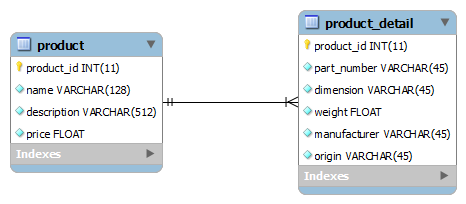
In this relationship, a product has one and only one detail information. Both the parent table (product) and child table (product_detail) share a same primary key (product_id). Thus it is called one-to-one association on a primary key. Let’s see how to model this relationship in Hibernate.
Software programs/libraries used this tutorial (you can use newer versions):
Table of content:
1. Creating database and tables
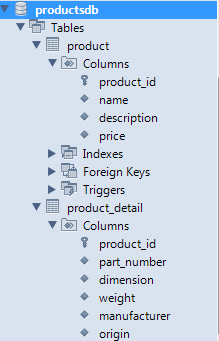
Let’s create a MySQL database called productsdb with two tables product and product_detail. If you are using MySQL Workbench, execute the following script in a SQL Editor:
create database productsdb; use productsdb; CREATE TABLE `product` ( `product_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(128) NOT NULL, `description` varchar(512) NOT NULL, `price` float NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`product_id`) ); CREATE TABLE `product_detail` ( `product_id` int(11) NOT NULL, `part_number` varchar(45) NOT NULL, `dimension` varchar(45) NOT NULL, `weight` float NOT NULL, `manufacturer` varchar(45) NOT NULL, `origin` varchar(45) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`product_id`) );
If you are using MySQL Command Line Client program, type the following command:
source Path\To\The\Script\File\MySQLscript.sql
You can find the MySQLscript.sql file the attached project or save it from the above script. The following screenshot shows structure of the newly created database:
2. Setting up Eclipse project
Using Eclipse IDE to create a standard Java project that has the following structure:
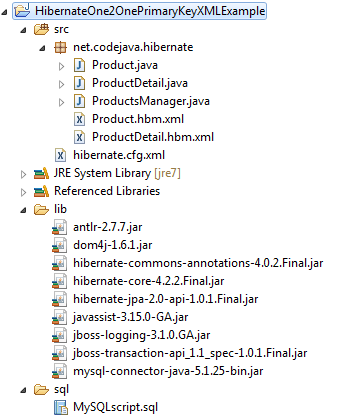
The project consists of the following files:
- Model classes: Product.java and ProductDetail.java
- Hibernate XML mapping files: Product.hbm.xmland ProductDetail.hbm.xml
- Hibernate XML configuration file: hibernate.cfg.xml
- Test program: ProductsManager.java
- Hibernate required JAR libraries and MySQL Connector Java driver:
- hibernate-core-4.2.2.Final.jar
- hibernate-commons-annotations-4.0.2.Final.jar
- mysql-connector-java-5.1.25-bin.jar
- jboss-transaction-api_1.1_spec-1.0.1.Final.jar
- hibernate-jpa-2.0-api-1.0.1.Final.jar
- jboss-logging-3.1.0.GA.jar
- antlr-2.7.7.jar
- dom4j-1.6.1.jar
- javassist-3.15.0-GA.jar
- MySQL script file: MySQLscript.sql
You can find the above Hibernate libraries under hibernate-release-VERSION\lib\required directory from Hibernate distribution archive.
3. Writing Hibernate Model Classes
To model the tables product and product_detail in Java, create the following two JavaBean-style classes:
File net\codejava\hibernate\Product.java:
package net.codejava.hibernate;
public class Product {
private long productId;
private String name;
private String description;
private float price;
private ProductDetail productDetail;
public Product() {
}
public ProductDetail getProductDetail() {
return productDetail;
}
public void setProductDetail(ProductDetail detail) {
this.productDetail = detail;
}
// other getters and setters
}
File net\codejava\hibernate\ProductDetail.java:
package net.codejava.hibernate;
public class ProductDetail {
private long productId;
private String partNumber;
private String dimension;
private float weight;
private String manufacturer;
private String origin;
private Product product;
public ProductDetail() {
}
public Product getProduct() {
return product;
}
public void setProduct(Product product) {
this.product = product;
}
// other getters and setters
}NOTES: Both the Product and ProductDetail classes have mutual reference to each other, through the properties productDetail and product, respectively. This is required for a bidirectional one-to-one association in which we can navigate the child entity from the parent and vice-versa, for example:
ProductDetail child = product.getProductDetail(); Product parent = detail.getProduct();
4. Writing Hibernate Mapping Files
Create two XML files corresponding to the two above model classes with the following content:
File net\codejava\hibernate\Product.hbm.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping package="net.codejava.hibernate">
<class name="Product" table="PRODUCT">
<id name="productId" column="PRODUCT_ID">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="name" column="NAME" />
<property name="description" column="DESCRIPTION" />
<property name="price" column="PRICE" type="float" />
<one-to-one name="productDetail" cascade="all" class="ProductDetail" />
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
File net\codejava\hibernate\ProductDetail.hbm.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping package="net.codejava.hibernate">
<class name="ProductDetail" table="PRODUCT_DETAIL">
<id name="productId" column="PRODUCT_ID">
<generator class="foreign">
<param name="property">product</param>
</generator>
</id>
<property name="partNumber" column="PART_NUMBER" />
<property name="dimension" column="DIMENSION" />
<property name="weight" column="WEIGHT" type="float" />
<property name="manufacturer" column="MANUFACTURER" />
<property name="origin" column="ORIGIN" />
<one-to-one name="product" constrained="true" class="Product" />
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>NOTES: The <one-to-one> element is used on both sides to enforce their one-to-one relationship, and the <generator class=”foreign”> element in the ProductDetail.hbm.xml file enforces that the product_detail table’s primary key is generated based on the product table’s primary key.
5. Writing Hibernate Configuration File
Following is content of the Hibernate configuration file hibernate.cfg.xml:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- Database connection settings -->
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/productsdb</property>
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.password">secret</property>
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<mapping resource="net/codejava/hibernate/Product.hbm.xml"/>
<mapping resource="net/codejava/hibernate/ProductDetail.hbm.xml"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>NOTES: Update the values of the properties connection.username and connection.password accordingly to your database username and password.
6. Coding a Test Program
Following is code of a demo program that obtains a Hibernate SessionFactory, persists a product (with detail) and lists all products:
package net.codejava.hibernate;
import java.util.List;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistryBuilder;
/**
* This program demonstrates using Hibernate framework to manage a
* bidirectional one-to-one association on a primary key.
* @author www.codejava.net
*
*/
public class ProductsManager {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// loads configuration and mappings
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
ServiceRegistryBuilder registry = new ServiceRegistryBuilder();
registry.applySettings(configuration.getProperties());
ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry = registry.buildServiceRegistry();
// builds a session factory from the service registry
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
// obtains the session
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction();
// creates a new product
Product product = new Product();
product.setName("Civic");
product.setDescription("Comfortable, fuel-saving car");
product.setPrice(20000);
// creates product detail
ProductDetail detail = new ProductDetail();
detail.setPartNumber("ABCDEFGHIJKL");
detail.setDimension("2,5m x 1,4m x 1,2m");
detail.setWeight(1000);
detail.setManufacturer("Honda Automobile");
detail.setOrigin("Japan");
// sets the bi-directional association
product.setProductDetail(detail);
detail.setProduct(product);
// persists the product
session.save(product);
// queries all products
List<Product> listProducts = session.createQuery("from Product").list();
for (Product aProd : listProducts) {
String info = "Product: " + aProd.getName() + "\n";
info += "\tDescription: " + aProd.getDescription() + "\n";
info += "\tPrice: $" + aProd.getPrice() + "\n";
ProductDetail aDetail = aProd.getProductDetail();
info += "\tPart number: " + aDetail.getPartNumber() + "\n";
info += "\tDimension: " + aDetail.getDimension() + "\n";
info += "\tWeight: " + aDetail.getWeight() + "\n";
info += "\tManufacturer: " + aDetail.getManufacturer() + "\n";
info += "\tOrigin: " + aDetail.getOrigin() + "\n";
System.out.println(info);
}
session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close();
}
}
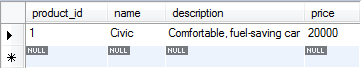
Output of the program:
Hibernate: insert into PRODUCT (NAME, DESCRIPTION, PRICE) values (?, ?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into PRODUCT_DETAIL (PART_NUMBER, DIMENSION, WEIGHT, ...
Hibernate: select product0_.PRODUCT_ID as PRODUCT1_0_, product0_.NAME as ...
Product: Civic
Description: Comfortable, fuel-saving car
Price: $20000.0
Part number: ABCDEFGHIJKL
Dimension: 2,5m x 1,4m x 1,2m
Weight: 1000.0
Manufacturer: Honda Automobile
Origin: Japan
Result in the product table:
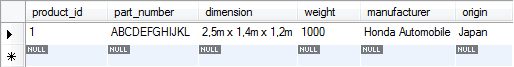
Result in the product_detail table:
You can get the sample project code on GitHub, or donwload in the Attachments section below.
Related Hibernate One-to-One Tutorials:
- Hibernate One-to-One Association on Primary Key Annotations Example
- Hibernate One-to-One Mapping with Foreign Key Annotations Example
- Hibernate One-to-One With Foreign Key XML Mapping Example
Other Hibernate Tutorials:
- Java Hibernate JPA Annotations Tutorial for Beginners
- Hibernate Hello World Tutorial for Beginners with Eclipse and MySQL
- Hibernate One-to-Many Using Join Table XML Mapping Example
- Hibernate Many-to-Many Association with Extra Columns in Join Table Example
- Hibernate Enum Type Mapping Example
- Hibernate Binary Data and BLOB Mapping Example
- Hibernate Query Language (HQL) Example
- Java Hibernate Reverse Engineering Tutorial with Eclipse and MySQL
- Hibernate Basics - 3 ways to delete an entity from the datastore
About the Author:
 Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Comments
Thanks in advance