Hibernate One-to-One With Foreign Key XML Mapping Example
- Details
- Written by Nam Ha Minh
- Last Updated on 12 December 2023 | Print Email
This Hibernate tutorial helps you learn how to implement a one-to-one association using XML mapping approach, by developing a sample Hibernate application that manages the following entity relationship:
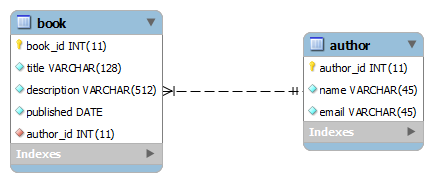
This relationship is supposing a book has only one author. It is called unidirectional one-to-one association on a foreign key in which the parent table (book) refers to child table (author) by a foreign key (author_id). The navigation is one-way from the book to the author: it’s possible to know author of a book, but not vice-versa. Note that this relationship is for the purpose of demo only.
The sample application in this tutorial is developed and tested in the following environment:
Let’s follow the steps described below.
Table of content:
1. Creating database and tables
First, we need to create a sample database with two tables: book and author. Execute the following SQL script in MySQL Workbench’s SQL Editor:
create database booksdb; use booksdb; CREATE TABLE `author` ( `author_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(45) NOT NULL, `email` varchar(45) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`author_id`) ); CREATE TABLE `book` ( `book_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `title` varchar(128) NOT NULL, `description` varchar(512) NOT NULL, `published` date NOT NULL, `author_id` int(11) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`book_id`), KEY `author_fk` (`author_id`), CONSTRAINT `author_fk` FOREIGN KEY (`author_id`) REFERENCES `author` (`author_id`) );
In case you are using MySQL Command Line Client program, run the following command:
source Path\To\The\Script\File\MySQLscript.sql
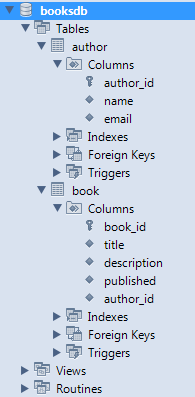
The MySQLscript.sql file can be found in the attached project or can be created from the above script. You would end up with a database called booksdb and two tables author and book as shown below:
2. Creating Eclipse project
Create a standard Java project in Eclipse IDE with the following structure:
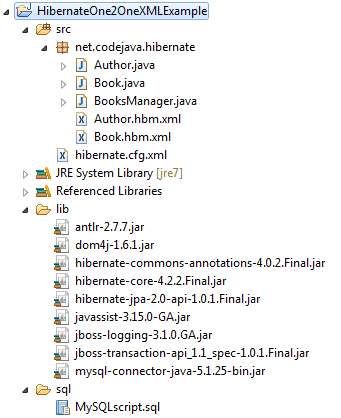
The project consists of the following files:
- Model classes: Author.java and Book.java
- Hibernate XML mapping files: Author.hbm.xmland Book.hbm.xml
- Hibernate XML configuration file: hibernate.cfg.xml
- Test program: BooksManager.java
- Hibernate required JAR libraries and MySQL Connector Java driver:
- hibernate-core-4.2.2.Final.jar
- hibernate-commons-annotations-4.0.2.Final.jar
- mysql-connector-java-5.1.25-bin.jar
- jboss-transaction-api_1.1_spec-1.0.1.Final.jar
- hibernate-jpa-2.0-api-1.0.1.Final.jar
- jboss-logging-3.1.0.GA.jar
- antlr-2.7.7.jar
- dom4j-1.6.1.jar
- javassist-3.15.0-GA.jar
- SQL script file for MySQL: MySQLscript.sql
The Hibernate required libraries can be found under hibernate-release-VERSION\lib\required directory from Hibernate distribution archive.
3. Creating Model Classes
We need to create two Java model classes according to two database tables: Author.java and Book.java. These are standard JavaBean-style classes.
File net\codejava\hibernate\Author.java:
package net.codejava.hibernate;
public class Author {
private long id;
private String name;
private String email;
public Author() {
}
public Author(String name, String email) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}
File net\codejava\hibernate\Book.java:
package net.codejava.hibernate;
import java.util.Date;
public class Book {
private long id;
private String title;
private String description;
private Date publishedDate;
private Author author;
public Book() {
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public Date getPublishedDate() {
return publishedDate;
}
public void setPublishedDate(Date publishedDate) {
this.publishedDate = publishedDate;
}
public Author getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(Author author) {
this.author = author;
}
}Note that the Book class has a property of type Author which denotes a has-a relationship in terms of object oriented programming.
4. Creating Hibernate mapping files
We need to tell Hibernate what are our model classes and how they associate with database tables by creating XML mapping files who names in the format of ModelClassName.hbm.xml. Create two XML files Author.hbm.xml and Book.hbm.xml with the following content:
File net\codejava\hibernate\Author.hbm.xml:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping package="net.codejava.hibernate">
<class name="Author" table="AUTHOR">
<id name="id" column="AUTHOR_ID">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="name" column="NAME" />
<property name="email" column="EMAIL" />
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
File net\codejava\hibernate\Book.hbm.xml:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping package="net.codejava.hibernate">
<class name="Book" table="BOOK">
<id name="id" column="BOOK_ID">
<generator class="native" />
</id>
<property name="title" type="string" column="TITLE" />
<property name="description" type="string" column="DESCRIPTION" />
<property name="publishedDate" type="date" column="PUBLISHED" />
<many-to-one name="Author" class="net.codejava.hibernate.Author"
column="author_id" unique="true" not-null="true"
cascade="all" />
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>Pay attention to the <many-to-one> element used in the Book.hbm.xml file. It is used to create the one-to-one relationship between the Book and Author entities. The attributes unique=”true” and not-null=”true” enforce this relationship.
5. Creating Hibernate Configuration File
To tell Hibernate to use which database type, connection details and the above mapping files, we need to create a hibernate.cfg.xmlfile:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- Database connection settings -->
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/booksdb</property>
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.password">secret</property>
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<mapping resource="net/codejava/hibernate/Book.hbm.xml"/>
<mapping resource="net/codejava/hibernate/Author.hbm.xml"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>This configuration specifies database driver type is MySQL and connection URL points to the database booksdb. You may change the database username and password according to yours. And finally we tell Hibernate to load two mapping files Author.hbm.xml and Book.hbm.xml.
6. Creating a test program
So far we have created all the nuts and bolts of configuration stuff. It’s time to write a simple test program that persists a Book entity to the database, gets it back and prints out the details. Here’s code of the BooksManager class:
package net.codejava.hibernate;
import java.util.Date;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistryBuilder;
/**
* This program demonstrates using Hibernate framework to manage
* a one-to-one entity relationship.
* @author www.codejava.net
*
*/
public class BooksManager {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// loads configuration and mappings
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
ServiceRegistryBuilder registry = new ServiceRegistryBuilder();
registry.applySettings(configuration.getProperties());
ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry = registry.buildServiceRegistry();
// builds a session factory from the service registry
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
// obtains the session
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction();
// creates a Book entity
Book newBook = new Book();
newBook.setTitle("Effective Java");
newBook.setDescription("Best practices for Java programming");
newBook.setPublishedDate(new Date());
newBook.setAuthor(new Author("Joshua Bloch", "joshua.bloch@gmail.com"));
// persists the book entity
Long bookId = (Long) session.save(newBook);
// gets the book entity back
Book book = (Book) session.get(Book.class, bookId);
System.out.println("Title: " + book.getTitle());
System.out.println("Description: " + book.getTitle());
Author author = book.getAuthor();
System.out.println("Author's name: " + author.getName());
System.out.println("Author's email: " + author.getEmail());
session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close();
}
}
Output of the program:
Hibernate: insert into AUTHOR (NAME, EMAIL) values (?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into BOOK (TITLE, DESCRIPTION, PUBLISHED, author_id) values (?, ?, ?, ?)
Title: Effective Java
Description: Effective Java
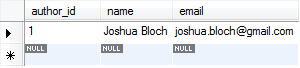
Author's name: Joshua Bloch
Author's email: joshua.bloch@gmail.com
Result in the Book table:
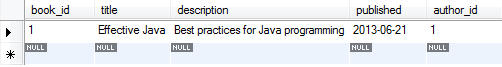
Result in the Author table:
You can get the sample project attached below, or check the code on GitHub.
Related Hibernate One-to-One Tutorials:
- Hibernate One-to-One Association on Primary Key Annotations Example
- Hibernate One-to-One Mapping with Foreign Key Annotations Example
- Hibernate One-to-One With Primary Key XML Mapping Example
Other Hibernate Tutorials:
- Java Hibernate JPA Annotations Tutorial for Beginners
- Hibernate Hello World Tutorial for Beginners with Eclipse and MySQL
- Hibernate One-to-Many Using Join Table XML Mapping Example
- Hibernate Many-to-Many Association with Extra Columns in Join Table Example
- Hibernate Enum Type Mapping Example
- Hibernate Binary Data and BLOB Mapping Example
- Hibernate Query Language (HQL) Example
- Java Hibernate Reverse Engineering Tutorial with Eclipse and MySQL
- Hibernate Basics - 3 ways to delete an entity from the datastore
About the Author:
 Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Comments
The specified file Book.hbm.xml is not found. Verify its path correctly.
Exception in thread "main" org.hibernate.MappingNotFoundException: resource: net.codejava.hibernate.Book.hbm.xml not found
Why is this happening??