Struts Beginner Tutorial with Convention Plugin (zero-configuration)
- Details
- Written by Nam Ha Minh
- Last Updated on 01 August 2019 | Print Email
1. The Struts Convention Plugin
This plugin enables zero-configuration for Struts application by enforcing the standard naming conventions. It comes with Struts distribution since version 2.1 and replaces the old CodebehindPlugin and Zero Config plugins. To use this plugin, simply put its jar file under WEB-INF\lib directory of your web application:struts2-convention-plugin-VERSION.jar
Or if you are using Maven, put the following entry in the pom.xml file:<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.struts</groupId>
<artifactId>struts2-convention-plugin</artifactId>
<version>VERSION</version>
</dependency>Now let’s explore some primary conventions. 2. Conventions for Struts action classes
- Scanning algorithm:
- The Convention plugin searches in the packages having the following words in their names: struts, struts2, action, or actions.
- Under the matching packages (and sub-packages), the plugin looks for the classes that are either:
- Implementing the com.opensymphony.xwork2.Action interface (either directly or extending its subclass com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport)
- Having their names end with Action.
- For example, the following classes will be found by the Convention plugin:
Classes
Reasons
net.codejava.struts.HelloWorldAction
Package name has “struts” and class name ends with “Action”.
net.codejava.actions.LoginAction
Package name has “actions” and class name ends with “Action”.
net.codejava.struts2.services.FileDownload
Package name has “struts2” and class implements the com.opensymphony.xwork2.Action interface.
- Action class to URL mapping convention:
- The plugin will map each action class to a specific URL, following this rules:
- Remove the word Action at the end of class name.
- Convert the uppercase letters to lowercase ones and add dashes among them.
- If there sub-packages after the words struts, struts2, action or actions, then the sub-package names will be converted to namespaces in the URL.
- For example, the above action classes will be mapped to the following URLs:
Action Classes
URLs
net.codejava.struts.HelloWorldAction
/hello-world
net.codejava.actions.LoginAction
/login
net.codejava.struts2.services.FileDownload
/services/file-download
- The plugin will map each action class to a specific URL, following this rules:
- Default action method: When an action’s URL is invoked, the plugin will invoke the action’s execute()method.
3. Conventions for results and JSP pages
The default location where the plugin looks for JSP pages corresponding to result codes returned from the action’s execute() method is WEB-INF/content directory. The following table shows how the plugin searches for the JSP pages based on the result codes:
URLs | Result codes | Matching JSP pages |
/hello-world | success | /WEB-INF/content/hello-world.jsp |
/hello-world | success | /WEB-INF/content/hello-world-success.jsp |
/login | success | /WEB-INF/content/login.jsp |
/login | error | /WEB-INF/content/login-error.jsp |
/login | input | /WEB-INF/content/login-input.jsp |
/services/file-download | success | /WEB-INF/content/services/file-download.jsp |
/services/file-download | error | /WEB-INF/content/services/file-download-error.jsp |
- If the plugin could not find a JSP page that matches a result code, it will find a JSP page for the “success” code instead. If there is no JSP page for “success” code, a 404 error will be returned.
- The plugin allows accessing JSP pages in the WEB-INF/content directory even when there are no associated action classes. This is called actionless results. For example, if we have a JSP file named hello-world.jsp in the WEB-INF/content directory, we can access it by this URL: /hello-world
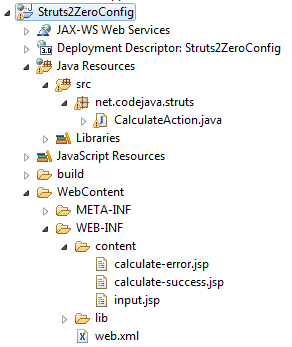
4. Code the input page
Here is source code of the input.jsp file under WEB-INF/content directory:<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>Input Form</title>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<h2>Calculate Division of X/Y</h2>
<s:form action="calculate" method="post">
<s:textfield name="x" label="Enter X" />
<s:textfield name="y" label="Enter Y" />
<s:submit />
</s:form>
</center>
</body>
</html>The form contains two text fields and it will call the action /calculate when submitted. 5. Code the Struts action class
Source code of the CalculateAction.java under the package net.codejava.struts:package net.codejava.struts;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
public class CalculateAction extends ActionSupport {
private int x;
private int y;
private float division;
public String execute() {
// calculates division
if (y == 0) {
return ERROR;
}
division = x / y;
return SUCCESS;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
public float getDivision() {
return division;
}
public void setDivision(float division) {
this.division = division;
}
}The action class declares two variables x, y and division with corresponding getters and setters. Its execute() method returns ERROR code if y equals to zero, otherwise returns SUCCESS code. That means we should create two JSP pages corresponding to these two result codes. 6. Code the result pages
Source code of the calculate-success.jsp (for SUCCESS result code) under WEB-INF/content directory:<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>Division Result</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>
Result of ${x} / ${y} is ${division}
</h3>
</body>
</html>And source code of the calculate-error.jsp (for ERROR result code) under WEB-INF/content directory:<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>Division Error</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>
Cannot divide by zero!
</h3>
</body>
</html> 7. Configure Struts in web.xml
Enable Struts' dispatcher filter in the web.xml as follows:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> <display-name>Struts2ZeroConfig</display-name> <filter> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <filter-class> org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter </filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> </web-app>
8. Required jar files for Struts
Add the following jar files into WEB-INF\lib directory (including the Convention Plugin’s jar file):- asm-3.3.jar
- asm-commons-3.3.jar
- asm-tree-3.3.jar
- commons-fileupload-1.2.2.jar
- commons-io-2.0.1.jar
- commons-lang3-3.1.jar
- commons-logging-1.1.1.jar
- commons-logging-api-1.1.jar
- freemarker-2.3.19.jar
- javassist-3.11.0.GA.jar
- ognl-3.0.6.jar
- struts2-convention-plugin-2.3.8.jar
- struts2-core-2.3.8.jar
- xwork-core-2.3.8.jar
9. Testing the Struts hello world application
Now let’s test the application we have built. Deploy it on Tomcat and type the following URL into browsers’ address bar:
http://localhost:8080/Struts2ZeroConfig/input
The input form is displayed. Enter two numbers as follows:
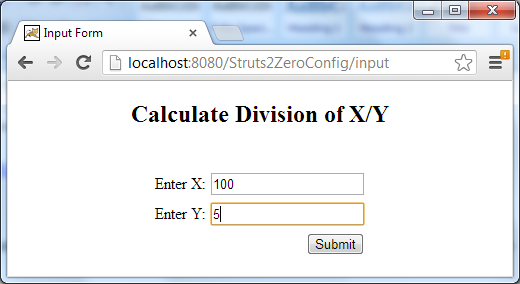
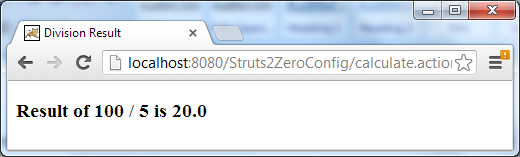
Then hit Submit, the result page is displayed:
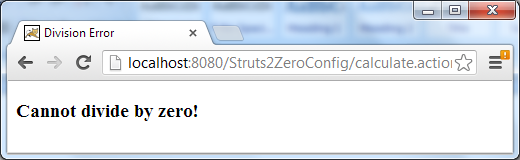
If we enter 0 for Y, the error page is displayed:
Related Struts Hello World Tutorials:
- Introduction to Struts framework
- Struts beginner tutorial (Eclipse + Tomcat + XML)
- Struts Beginner Tutorial with Annotations
Other Struts Tutorials:
- How to handle exceptions in Struts
- How to use log4j in Struts
- Send e-mail with attachments in Struts
- Struts File Download Tutorial
- Struts File Upload Tutorial
- Struts - Spring - Hibernate Integration Tutorial
About the Author:
 Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He began programming with Java back in the days of Java 1.4 and has been passionate about it ever since. You can connect with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos on YouTube.
Comments